
Hello {{First Name|there}},
This week, we’re exploring Ozempic, a groundbreaking medication that goes beyond blood sugar control to reveal surprising benefits for vascular health.
You may know Ozempic as a medication for managing blood sugar and promoting weight loss, but did you know it also supports your cardiovascular system? Let’s explore how this groundbreaking treatment mimics the body’s natural hormones, its potential benefits, and the foods that naturally promote these pathways.
What Is Ozempic and What Does It Do?

Ozempic’s active ingredient is semaglutide, a medication that mimics the natural hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). GLP-1 is produced in the gut and plays an important role in regulating metabolism, appetite, and blood sugar. What makes it remarkable is its widespread activity throughout the body, thanks to GLP-1 receptors, which are found in areas like the pancreas, brain, heart, digestive tract, and blood vessels.
When semaglutide binds to these receptors, it produces several beneficial effects:
Stimulates insulin release: In the pancreas, semaglutide helps regulate blood sugar by prompting insulin secretion when blood sugar levels are high. This ensures glucose is properly absorbed by cells for energy.
Suppresses glucagon secretion: Semaglutide also suppresses the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar. By doing so, it prevents sudden spikes in glucose levels.
Slows digestion: In the stomach, semaglutide slows the emptying of food into the small intestine. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and promotes a feeling of fullness after meals.
Reduces appetite: In the brain, semaglutide activity influences hunger signals, reduces cravings, and supports weight loss by helping you eat less.
Beyond its metabolic effects, researchers are uncovering how semaglutide may support cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, improving blood vessel function, and lowering the risk of artery-related conditions. Next, let’s examine how semaglutide benefits blood vessels and heart health.
Semaglutide and Vascular Health
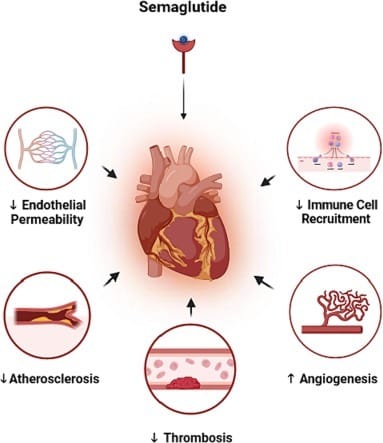
Image Source: Yaribeygi et al., 2024.
Semaglutide does more than regulate blood sugar—it actively supports blood vessel health and reduces risks associated with cardiovascular disease. According to research published in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, semaglutide helps maintain healthy circulation through several key mechanisms:
Endothelial Permeability: Strengthening the Blood Vessel Lining
The endothelium is the thin, protective layer inside blood vessels that regulates what enters and exits the bloodstream. When this layer becomes overly permeable, it allows harmful substances to pass through, leading to inflammation, leakage, and vessel damage.
Semaglutide activates GLP-1 receptors in endothelial cells, helping reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. These effects support the endothelium's integrity, keeping blood vessels strong, flexible, and efficient at transporting oxygen and nutrients.
Preventing Atherosclerosis: Slowing Plaque Buildup in Arteries
Atherosclerosis occurs when plaque builds up in arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. This process begins with chronic inflammation, which damages artery walls and creates a site for plaque to form.
By lowering levels of pro-inflammatory molecules like TNF-α and IL-6, semaglutide may reduce inflammation in blood vessel walls. This can help slow plaque development, maintain smooth and unobstructed blood flow, and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Immune Cell Recruitment: Regulating Immune Activity to Protect Blood Vessels
The immune system plays a vital role in healing, but overactive immune cells can damage blood vessels instead of repairing them. For example, neutrophils, a type of immune cell, can drive inflammation when they overreact in the vascular system.
Semaglutide appears to modulate immune responses by influencing neutrophil activity and reducing excessive immune cell recruitment to blood vessels. This helps prevent unnecessary inflammation and ensures arteries and capillaries remain healthy and functional.
While semaglutide offers a medical breakthrough, did you know that your diet can also play a role in activating GLP-1? Let’s explore how certain foods can naturally support these pathways.
Foods That Trigger GLP-1 Receptors Like Ozempic

According to a review published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, dietary choices may help influence GLP-1 activity, particularly in individuals with metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. The review highlights that what we eat—especially fiber and protein—may help the body increase GLP-1 levels after a meal, though researchers are still studying which nutrients have the strongest effect.
Fiber: Fueling GLP-1 Through Gut Fermentation
Fiber-rich foods play a role in enhancing GLP-1 activity by interacting with the gut microbiome. When soluble fiber reaches the colon, it undergoes fermentation by gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These SCFAs signal to L-cells, specialized cells in the gut lining responsible for producing GLP-1, prompting its release into the bloodstream.
Despite a recommended daily fiber intake of around 30 grams, the national average intake is only about 12–15 grams—falling far below optimal levels. Excellent sources include oats, barley, apples, flaxseeds, Brussels sprouts, and beans.
Protein: Sustaining GLP-1 and Prolonging Fullness
Protein intake also contributes to GLP-1 activation. As proteins are broken down during digestion, they release peptides, which can directly stimulate GLP-1-producing cells in the gut. Including protein-rich foods such as lean meats, fish, eggs, Greek yogurt, tofu, and legumes like chickpeas and lentils in your meals may help enhance GLP-1 activity, supporting appetite regulation and blood sugar control.
You can support metabolic health and overall well-being by consistently including these nutrient-dense foods in a balanced diet.
Which of the following is a function of GLP-1 in the body?
Looking Ahead
GLP-1’s role in metabolic and vascular health continues to be an exciting area of research. By understanding how medications like semaglutide work alongside dietary strategies, we gain valuable insight into improving blood sugar control, reducing inflammation, and supporting heart health.
Stay connected with us to receive the latest on evidence-based research, advancements in healthcare, and practical tips.
Best wishes,
- The Angiogenesis Foundation


